
Under either system, the allocation of goods available for sale to the cost of sales and ending inventory is the same if the inventory valuation method used is either specific identification or FIFO. Both systems will also result in education or student tax credits you can get on your tax return different allocations to the cost of sales and ending inventory if the LIFO method is used in inventory valuation. However, the need for frequent physical counts of inventory can suspend business operations each time this is done.
- The three cost flow assumptions that businesses use for this are FIFO, LIFO, and the Weighted Average Cost (WAC).
- Further, an organisation with several retail locations may find it is easier to control inventory when there’s a regularly updated database of products.
- That’s because every transaction is recorded in real-time under a perpetual inventory system.
- A physical inventory count requires companies to do a manual “stock-check” of inventory to make sure what they have recorded on the books matches what they physically have in stock.
- The remainder of the cost of goods available is reported on the income statement as the cost of goods sold.
Perpetual Inventory System
With perpetual inventory, overstatements, also called phantom inventory, and missing inventory understatements can be kept to a minimum. Perpetual inventory is also a requirement for companies that use a material requirement planning (MRP) system for production. Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) do not state a required inventory system, but the periodic inventory system uses a Purchases account to meet the requirements for recognition under GAAP.
Comparing Perpetual LIFO and Periodic LIFO
Therefore, a moving average system must be programmed to update the average whenever additional merchandise is acquired. However, the need for frequent physical counts of inventory cansuspend business operations each time this is done. There are morechances for shrinkage, damaged, or obsolete merchandise becauseinventory is not constantly monitored. Since there is no constantmonitoring, it may be more difficult to make in-the-moment businessdecisions about inventory needs.
Example of the Difference between Perpetual LIFO and Periodic LIFO
Further, an organisation with several retail locations may find it is easier to control inventory when there’s a regularly updated database of products. Take, for example, a tool retailer that has a customer looking for a specific type of wrench, one that is rarely requested and sold. Using a perpetual system, it has real-time information about which site may have one in stock so the customer can go get his wrench quickly instead of driving from store to store looking for it. Cameron Ltd. is an electronic retailer company that uses a tracking system to identify every single item in its inventory. The following table illustrates the company’s purchases and sales of LCD screens during the month of April 2017. Assume that the company had no inventory of LCD screens at the beginning of the period and that it sells each unit for $700.
Example of Difference Between Periodic LIFO and Perpetual LIFO
While both the periodic and perpetual inventory systems require a physical count of inventory, periodic inventorying requires more physical counts to be conducted. This updates the inventory account more frequently to record exact costs. Knowing the exact costs earlier in an accounting cycle can help a company stay on budget and control costs. While both the periodic and perpetual inventory systems requirea physical count of inventory, periodic inventorying requires morephysical counts to be conducted. Knowing the exact costsearlier in an accounting cycle can help a company stay on budgetand control costs. The perpetual inventory system gives real-time updates and keeps a constant flow of inventory information available for decision-makers.
EOQ is a formula that managers use to decide when to purchase inventory based on the cost to hold inventory as well as the firm’s cost to order inventory. Businesses that use a perpetual inventory system typically employ cycle counting or the process of physically counting a portion of inventory to use as a baseline to check the accuracy of the perpetual system. Under Periodic LIFO, the inventory and COGS are updated at the end of the accounting period, not continuously. Perpetual inventory methods are increasingly being used in warehouses and the retail industry.
When a company sells products in a perpetual inventory system, the expense account increases and grows the cost of goods sold (COGS). This includes the materials and labor costs but not distribution or sales expenses. The perpetual system may be better suited for businesses that have larger, more complex levels of inventory and those with higher sales volumes.
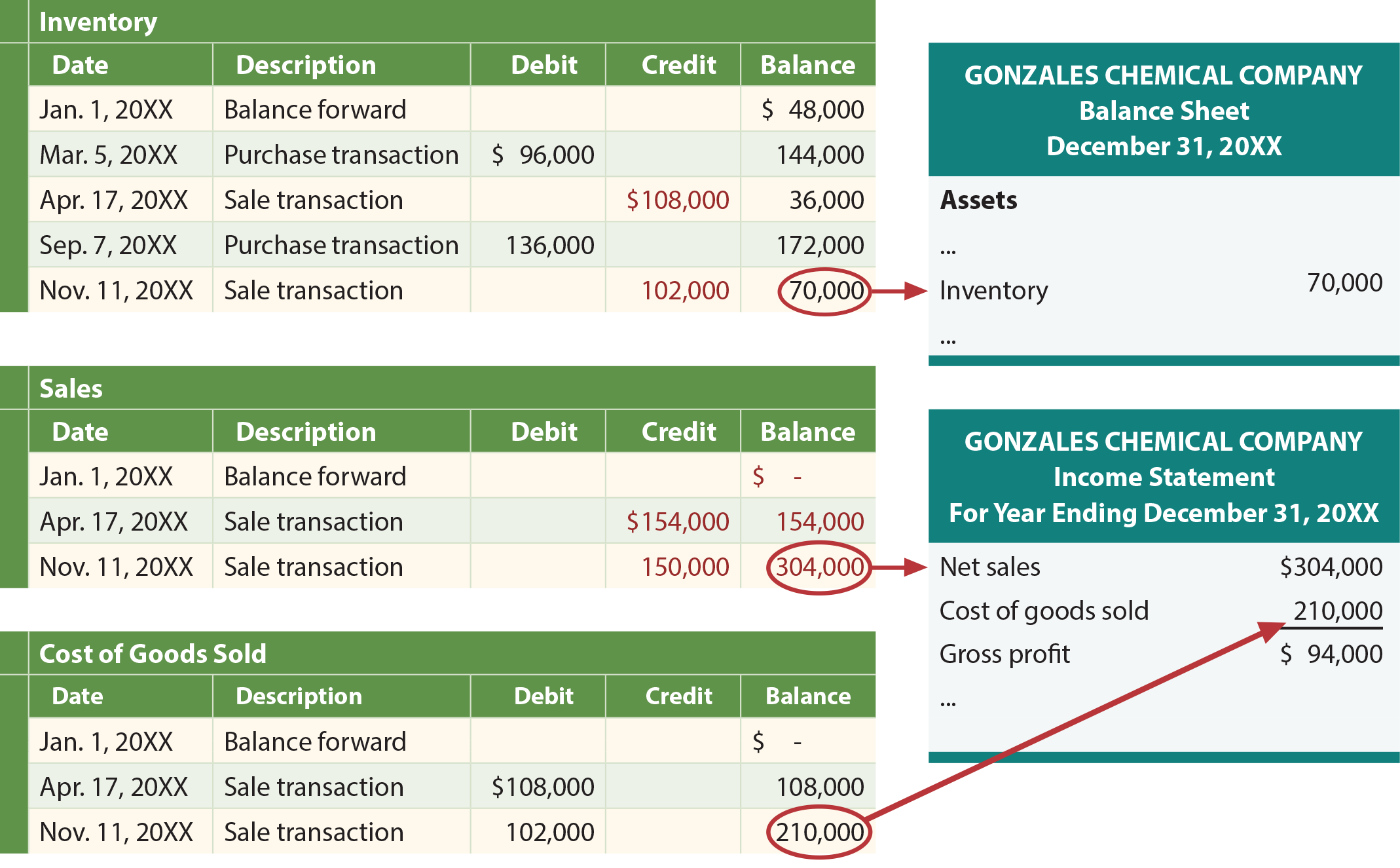
A periodic inventory system is a simplified system for calculating the value of an ending inventory. It only updates the ending inventory balance in the general ledger when a physical inventory count is conducted. Since physical inventory counts are time-consuming, few companies do them more than once a quarter or year. In the meantime, the inventory account in the accounting system continues to show the cost of the inventory that was recorded as of the last physical inventory count. This means that the inventory valuation in the accounting records will be inaccurate, except when a physical count is performed. At the end of the period, a perpetual inventory system will have the Merchandise Inventory account up-to-date; the only thing left to do is to compare a physical count of inventory to what is on the books.
She will use this information to calculate the ending inventory and COGS for the period. See the ledger below for transactions for Acetone in Jan. using a weighted average. FIFO (first-in, first-out) is a cost flow assumption that businesses use to value their stock where the first items placed in inventory are the first items sold.
Once the COGS balance has been established, an adjustment is made to Merchandise Inventory and COGS, and COGS is closed to prepare for the next period. Once the COGS balance has been established, an adjustment ismade to Merchandise Inventory and COGS, and COGS is closed toprepare for the next period. Under a periodic LIFO system, however, layers are only stripped away at the end of the period, so that only the very last layers are depleted.